Seismic retrofit is the modification of existing structures to make them more resistant to seismic activity, ground motion, or soil failure due to earthquakes.
Base isolation is one of the most popular means of protecting a structure against earthquake forces. It is a collection of structural elements which should substantially decouple a superstructure from its substructure resting on a shaking ground thus protecting a building or non-building structure’s integrity.
The isolation can be obtained by the use of various techniques like rubber bearings, friction bearings, ball bearings, spring systems and other means. It is meant to enable a building or non-building structure to survive a potentially devastating seismic impact through a proper initial design or subsequent modifications (Wikipedia, 2019).
Chilean Engineers Applying Base Isolation System
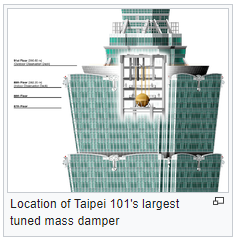
A tuned mass damper is a device mounted in structures to reduce the amplitude of mechanical vibrations. Their application can prevent discomfort, damage, or outright structural failure.
Tuned mass dampers stabilize against violent motion caused by harmonic vibration. A tuned damper reduces the vibration of a system with a comparatively lightweight component so that the worst-case vibrations are less intense. Roughly speaking, practical systems are tuned to either move the main mode away from a troubling excitation frequency, or to add damping to a resonance that is difficult or expensive to damp directly. Mass dampers are frequently implemented with a frictional or hydraulic component that turns mechanical kinetic energy into heat (Wikipedia, 2019).